Strategic Planning Process
In Marketing Activity we define marketing process as:
1. Analyze Marketing Opportunities
a. Analysing Marketing Opportunities



 FORMULATING MARKETING OBJECTIVES
FORMULATING MARKETING OBJECTIVES
 What if we find that our products are wrongly positioned
What if we find that our products are wrongly positioned

 Planning Product Strategies No 1- Product Attribute Strategies(PAS)
Planning Product Strategies No 1- Product Attribute Strategies(PAS)
 Length: Total Number of items
Length: Total Number of items

 MARKETING STRATEGIES NO. 3- PRICING STRATEGIES
MARKETING STRATEGIES NO. 3- PRICING STRATEGIES

Step 1. : Define Company’s Mission
Step 2 : Set organization goals and objectives
Step 3 : Design Business Portfolios
Step 4: Decide Various Functional Activities ( One is marketing)
In Marketing Activity we define marketing process as:
1. Analyze Marketing Opportunities
a. Analysing Marketing Opportunities
i. Understanding Marketing Environment
ii. Conducting Marketing Research to validate Ideas (Know consumer/buyer behavior to identify their needs, wants and demands)
iii. Identifying Customer Segments and target the most potential segments
iv. Formulating Marketing Objectives
- Design Marketing Strategy
- Product Positioning
- Product Planning
- Pricing Decisions
- Placement Decisions
- Promotion Planning
- Manage Marketing Effort- It includes analysis, planning, organizing, directing and controlling.
We discuss in Detail these one-by-one
- UNDERSTANDING MARKETING ENVIRONMENT
Actors and forces outside marketing that affects marketing manager ability to develop and maintain successful transactions with his target customers

- MARKETING RESEARCH AND CONSUMER BEHAVIOUR
please see the respective sections
- MARKET SEGMENTATION
It is the process of dividing the consumer market into distinct groups of potential buyers with homogenous needs.
How to do It
We start dividing the market on specific characteristics of which are most important for that product, followed by next most important and so on.
Why to Do it
- to offer product and services
- For repositioning
- For Advertisement
How much to Segment
- Mass Marketing
- Segment Marketing
- Niche Marketing
- Specific Subgroups that may seek a special combination of benefits
- Micromarketing
- Local
- Individual
What are those specific Characteristic
- Geographic
- “ Hero impact” for cities
- Demographic
- Age, Size, Life Cycle ( Lakme Orchid- Upper income bracket)
- Psychographic
- Social Class ( Atlas Rebel), VALS classification
- Behavioral
- Benefit, Occasion, user frequency etc. (Tooth paste- sparkling, eating, tooth decay, etc.)
What are the things to be kept in mind while segmenting
Market Segment must be
- Measurable – “Segment “ of “Rebel” women smokers
- Sustainable- Motorcycle for people less than 4 ft.
- Accessible- Effectiveness of reaching and surviving a market
- Actionable- You may not reach to large segment for a new brand of soap- don’t have resources.
3 TARGETING
Targeting is essentially a two stage process. It involves:
- Evaluating the market segment
- Selecting the marketing segments considering opportunity and renounces.
How to Evaluate Market Segment
To evaluate a market segment, you have to look at three things:
- Segment Size and Growth
- It must have the right size and growth rate for the company to enter.
- Segment Structure Effectiveness
- Organisation – Core Competency
How to select a Target Market
1. Undifferentiated Marketing (Mass Marketing) (Tata salt)
see fig 3

2. Differentiated Marketing (HLL)
see fig 4

3. Concentrated Marketing, like Caterpiller Tractor, JCB, Lakme .
see fig 5
 FORMULATING MARKETING OBJECTIVES
FORMULATING MARKETING OBJECTIVES
Achieve a 10% market share in the soap market in the first year of the launch.
SMART APPROACH
S- Specific
M- Measurable
A- Attainable
R- Realistic
T- Time Bound.
MARKETING STRATEGIES
Marketing Strategies No. 1. : PRODUCT POSITIONING
Positioning is the act of designing the company’s offer so that it occupies a distinct and valued place in the mind of the consumer.
It thus
– differentiates a product from its competitors- Godrej with “PUF”
- Creates a preference for that product- “Hero Hond”- Fill it, shut it, forget it.
How to position
- By parentage- TATA
- By usage- Burnol
- By User- Cerelac for infants
- Against Competition- Hertz
- By attributes or features- Godrej with “PUF”
- By Benefit- “fill it, shut it, forget it”.
- BY 4 Ps
- Product- HH Sleek
- Price- Louis Phillipe
- Place- Designer Wear
- Promotion- A personal gift- Amul Chocolates
How do we know how our product is positioned
- By perceptual Mapping
- Mapping of the perception of a consumer on certain parameters. It offers an insight into the mind of market and reveals where a brand stand v/v competition.
See figure6
 What if we find that our products are wrongly positioned
What if we find that our products are wrongly positioned
We reposition it: Wills easier “comb of tobacco for mature adults” has now changed to more younger, more romantic – “made for each other”
Marketing Strategies No. 2- PLANNING PRODUCT STRATEGIES
Product
Anything that can be offered to a market for acquisition, attention, use or consumption that might satisfy a need or want. It includes physical objects, services, persons, places, organizations and ideas.
See fig7

Product Classification
See Fig 8
 Planning Product Strategies No 1- Product Attribute Strategies(PAS)
Planning Product Strategies No 1- Product Attribute Strategies(PAS)- (PAS)Product
i. Design and Color
ii. Specification / feature
iii. Product quality
- (PAS)Branding Strategies
Brand: Name, term, symbol or a special design or some combination of these that is designed to identify the goods or services of one seller or a group of sellers.
Characteristics of Brand Name
- Short and Crisp (Lux and Liril)
- Unique ( Kodak, Xerox)
- Relevant ( Band-Aid, Good Night)
- Flexible ( Vicks)
Branding Strategies
- Blanket Family Name
- Individual Brand Name
- Combination
Brand Extension
- Using existing brand name to launch new or modified product- Vicks, Cough Syrup
Reasons
- Instant recognition
- Saves time and cost
- Gains an edge over competition
Criteria for Brand Extension
- Compatible with original brand and image
- Existing brand should have “ value perception”
- (PAS) Packaging Strategies
Packaging- The activities of designing and producing the container or wrapper for a product.
Why Packaging
- Differentiates product from competitors
- Easy Identification
- Acts as silent sales person at retail shelves
- Can add to image and value (transparent, ecological and reusable)
- Add customer convenience
- Protects the product
Packaging Strategies
- Family Packaging- Nestle, Maggi color
- Reusable Packaging- Coke glass bottle
- Multiple Packaging- Several units are packed.
- (PAS) Labelling
A label is that part of the product that carries information about the product, the manufacturers and marketing organization
- some times new information eg. Venkies Chicken Packs carries receipes
- (PAS) Product Support Services
- Return Policy
- Guarantee
- Warrantee
Planning Product Strategies No. 2– Product Mix Decision
Product Mix- Entire range of products
Product Mix Strategies
Contraction
Low profit generating items are eliminated . Voltas got out of Ketchup (Volfarm)
Expansion
No. of lines or depth within a line are increased. Like HLL increased tooth paste variants.
Planning Product Strategies No. 3- Product Line Strategis
Product Line: A group of products that are closely related because
- They function in a similar mananer
- Are mostly sold to the same customer group
- Are marketed through the same channel
- Fall within a given price range
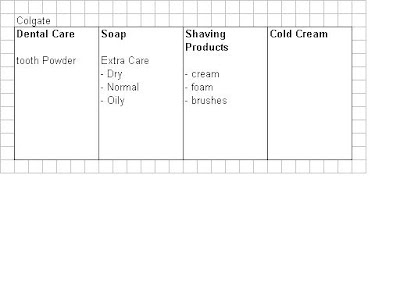
See fig9
 Length: Total Number of items
Length: Total Number of items
Width: Total No. of product lines
Depth: No. of items in each product line
Consistency: How closely related the various product lines are in end use/ production requirements/ channels etc.
Why product line strategies
- To create entry barriers for competitors
- To offer a comprehensive range of products
- Optimise productivity
- Keep abreast of changing customer needs
Line Strategies
- Line Strategies: Add to product line more items
- Line Filling: Introduce more sizes and variants of same items
- Line Modernisation: Upgrade 486 to Pentium
- Line Pruning: Eliminate unprofitable and technologically inferior items
Planning Product Strategies No. 4- New Product Development Strategies
New Product Development: The development of original product, product improvement, product modification and new brands through the firms own R& D efforts.
Why so many products fail
It starts with the whole marketing process- anything can go wrong with that process.
Process of New Product Development
- Idea Generation: The systematic search for new product ideas
- Idea Screening: Screening new product ideas in order to spot good ideas and drop poor ones as soon as possible.
- Generation of Product Concept: A detailed version of the new product idea stated in a meaningful consumer terms: Bournvita: Tasty health drink
- Concept Testing: Testing new concepts within a group of target consumers to find out if concepts have strong consumer appeal.
- Market Strategy Development : Designing an initial marketing strategy for a new product based on product concept.- positioning/price/product/place/ promotion
- Business Analysis: A review of the sales costs and profit projections for a new product to find out whether there factors satisfy company’s objectives.
- Product Development: Converting to actual development of product.
- Market Testing: Testing in realistic market settings.
- Commercialisation: Introducing a new product into the market.
Planning Product Strategies No. 4- PLC strategy analysis
See fig 10

See fig 11
 MARKETING STRATEGIES NO. 3- PRICING STRATEGIES
MARKETING STRATEGIES NO. 3- PRICING STRATEGIES
Price
Sum of money needed to acquire a product and its accompanying service.
Why pricing is important
- Influences rent, salaries, interest and service
- Influences market demand, share and revenue
- Determines what will be produced and who gets what
- Related to quality
How pricing is determined
See fig 12

What are pricing Strategies
- Marketing Penetration
- Market Skimming
- Competitive Pricing
- Survival Pricing
- Psychological Pricing
- Loss- Leader Pricing
MARKETING STRATEGIES NO. 4- PLACEMENT STRATEGIES
The objectives of placement or distribution is simply to provide maximum convenience by ensuring that the product/ services
- reaches the planned number of consumers
- in the desired time frame
- at a reasonable cost
eg. Shampoo- distributors, Eureka Forbes- directly, Nestum – Professionals, and Mcdonalds- Directly Franchisees.
Why Placement is important
- A company cannot reach all the customer
- Lack of financial resources
- Low ROI on own channel- can concentrate on your business
- Middleman capability- superior efficiency
- Middleman keep limited quantity with huge variety, while company can keep huge quantity with limited variety. So middle man can benefit from keeping a companies products.
What are the things that you consider while selecting Distribution Channels
Choice of a Distribution Channel depends upon
- Target Market
- No. of Customers
- Geographical Concentration
- Order Size
- Customer Convenience
- Product Consideration
- Unit Value
- Perishability
- Technical Nature
- Company Consideration
- Financial
- Managerial Capability
- Desire to Control Channels
- Middleman Consideration
- Experience
- Knowledge of Segment
- Efficiency
- Additional value that they can provide.
How much to distribute
Distribution Intensity
- Intensive Distribution – FMCG
- Selective Distribution – “shopping” or “speciality goods”
- Exclusive Distribution- Raymond
MARKETING STRATEGY NO. 5- PROMOTION STRATEGY
Promotion
The marketing tool which involves various methods of communicating persuasively with the customers in order to arouse/ reinforce his interest in the product.
Objectives of any Marketing Communication Exercise
The AIDA Model
Promotion Mix
- Advertising
- Sales Promotion
- Public Relation
- Personal selling
ADVERTISING
Advertising can be
- Product
- Financial
- Corporate
- Social
Stages of Advertising
- Pioneering
- Competitive
- Retentive
- No
How to Plan Advertising
- Mission
- Information Objective
- Persuasive Objective
- Reminder Objective
- Market
- Demographic, Geographic, Psychographic, Behavioural
- Money
- Desired reach/ frequency/ competition/ % to sales ratio
- Message
- Theme- Emotional, rational, moral
- Presentation- visual, color, model, copy ( Headlines, body, signoff, music, mnemonic)
- Source
- Media
- Electronic
- Print ( Continuous, fleeting, pulsing)
- Outdoor
- Measurement
- Direct Rating
- Portfolio Test
SALES PROMOTION
It’s a marketing activity aimed at encouraging purchase of a product through added impetus to buy.
Objective
- Overcome decline in sales
- Generate Trials
- Increase sales of slow moving products
- Counter Competitive activities
- Reduce excess pile up of inventory
- Liquidate old stocks
- Make consumers buy more than usual
Types
- Trade Promotion
- Consumer Promotion
o Coupon
o Free Gift
o Price-off
o Reusable Pack
o Bonus Pack
o Contest/ games
o Installment offers
Sales promotion Campaign
- Defining objectives
- Design Campaign
o Target
o Type
o Duration
o Vehicle
o Cost
- Implement
- Evolution
PR OR PUBLICITY
Mass Communication/ non-paid form/ impersonal. Third person reference more credible- wider publicity at no cost. Also includes sponsoring a program
PERSONAL SELLING
Face to face/ 2-way/ immediate response/ very expensive.

No comments:
Post a Comment